Description
The REALQUALITY ResP-HSM is an IVD for the identification of Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Moraxella catarrhalis in respiratory samples from patients with signs and symptoms of respiratory infection by PCR Real-Time.
Product Characteristics
- The device is validated on DNA extracted from various samples types
- The assay requires only 5 µL of DNA extracted
- Validated on main Real time PCR instruments
- The automatic format of the assay can be used used on GENEQUALITY automatic platforms
- Easy interpretation of results with AB Genius Report software
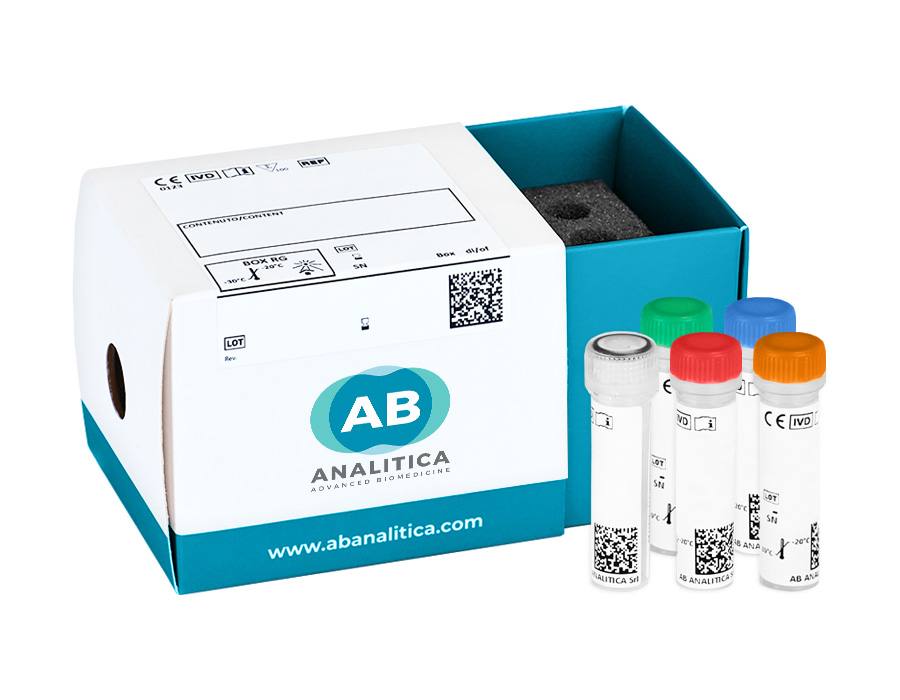
Kit content
Kit content:
- Freeze-dried reagents for real time PCR amplification
- Extraction control (freeze-dried)
- Positive control (freeze-dried)
- Negative control
- Rehydration Buffer (solution to reconstitute the freeze-dried products)
- Water RNAse/DNAse free
Further Information
Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Moraxella catarrhalis are the most common bacterial pathogens in upper and lower respiratory tract infections. In an individual with pre-existing conditions, the host’s immune system responds to the infection by causing oedema and swelling. If antimicrobial treatment does not eradicate invading organisms and successfully halt the progression of the infection, the patient may develop recurrent or chronic disease.
H. influenzae is a pleomorphic Gram-negative coccobacillus responsible for a wide variety of airway mucosal infections and invasive diseases such as bacterial meningitis, bacteremia, septic arthritis, pneumonia, tracheobronchitis, otitis media, conjunctivitis, sinusitis, and acute epiglottitis. These infections, as well as endocarditis and urinary tract infections, can occur in adults, although much less commonly.
S. pneumoniae, also called pneumococcus, is a gram-positive bacterium belonging to the genus Streptococcus and is the most common cause of pneumonia and meningitis. Pneumococcus is a habitual colonizer of the upper respiratory tract and, in addition to pneumonia, causes frequent associated respiratory tract infections, such as otitis media, sinusitis, and bronchitis. Young children, the elderly, and immunodeficient patients are at particular risk of developing pneumococcal infections.
M. catarrhalis is a non-encapsulated Gram-negative diplococcus and an opportunistic human pathogen. A common commensal of the upper respiratory tract, M. catarrhalis was once considered nonpathogenic but is now recognized as one of the most common causes of respiratory tract infection (RTI).
Ordering Information
| Code | Product | PKG |
|---|---|---|
| RQ-148-6A | REALQUALITY ResP-HSM - Manual and automatic format | 96 tests |